TN TFT Structure
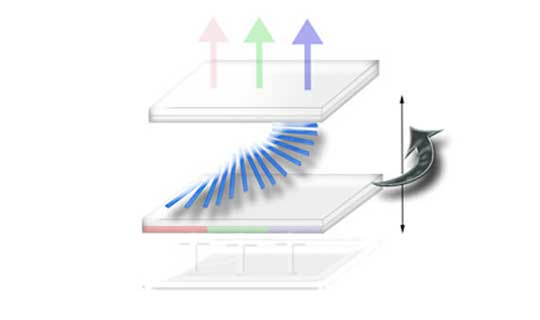
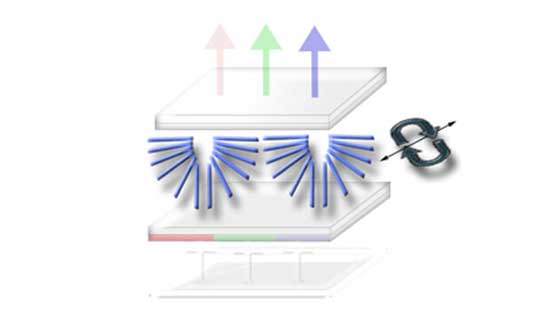
Twisted Nematic ("TN") Thin-Film Transistor ("TFT") Displays fundamentally operate with Liquid Crystal fluid much like their monochrome counterparts. The TN fluid rotates horizontally within the planes of glass with thread-like alignment allowing light through. Linear Polarizing films on the top and bottom will control the passage of light, minimize unwanted light and improve contrast of the display.
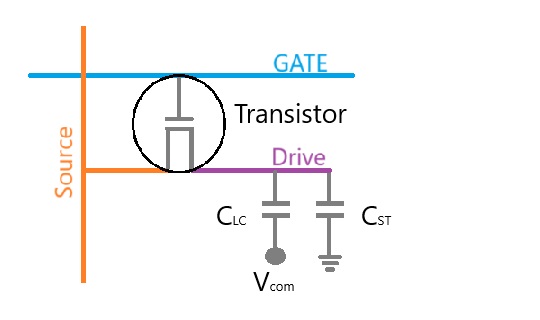
The TFT layer adds an important function of electrically powering all pixels separately from the the logic drive. The response of traditional LC fluid is too slow for video frame rates, so the need of having each pixels in parallel operation is necessary. The majority of TFT displays are full color display designs. A color filter is used so that white backlighting can accomplish primary colors. The most common solution will be Red, Green, and Blue ("RGB") sub-pixel patterns that are independently addressable.